So, how does programmatic advertising work anyway?
It’s surprisingly easy once you’ve grasped the fundamentals. This handy introduction to how things work in the programmatic ad niche will take you from zero to in-the-know, super-fast.
This is a pretty comprehensive guide for updating what you know.
This is a great post for marketers who need clarity on some key inner-workings, or for brand advertisers who want to brush up on their programmatic terminology.
It’s also perfect if you’ve never investigated programmatic marketing before, and your curiosity level is peaking like a whistling stovetop kettle from the sixties.
Here’s your chance to get the authentic, no-holds-barred, clean and simple scoop on how programmatic advertising really works.
Editor’s Note: We recommend reading our post, ‘What is Programmatic Advertising’ first, which details what it is, and why you should be excited about it. Otherwise, let’s streak ahead to the how.
- A Brief Introduction to Programmatic Advertising
- The Programmatic Advertising Process
- How Programmatic Advertising Works From Start to Finish
- The Elements of Programmatic Advertising
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
- Optimizing Your Campaigns With Real-Time Bidding
- Using Data in Programmatic Advertising
- Targeting and Relevance in Your Ad Campaigns
- The Creative Side of Programmatic Campaigns
- Achieving Campaign Goals With Programmatic
- Sharing How Programmatic Advertising Works
- TL;DR – What Have We Learned
A Brief Introduction to Programmatic Advertising
Digital ads are everywhere.
On connected TV, your favorite blog, your Facebook page, your search engine – they’re even in every app on your phone. Back in the 70’s, people were exposed to about 500 ads a day.
These days, the average American sees between 4000-10,000 ads daily. That’s an ad every 15 seconds, if you’re counting.
A lot of these ads don’t work. According to eMarketer, about one-fourth of all advertising budgets are wasted. As a result, marketers are constantly trying to optimize their ad spend.
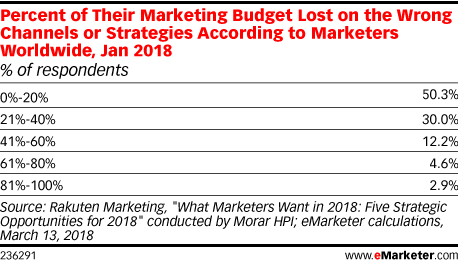
The most advanced way to do this is with programmatic advertising.
Definition:
Programmatic advertising is the automated buying and selling of digital ad space on the internet.
In other words, digital ads are automatically traded through software.
It’s mostly done in real-time using an auction-style system – but this varies. If you want more context, do head over to our first post, “What is Programmatic Advertising?“
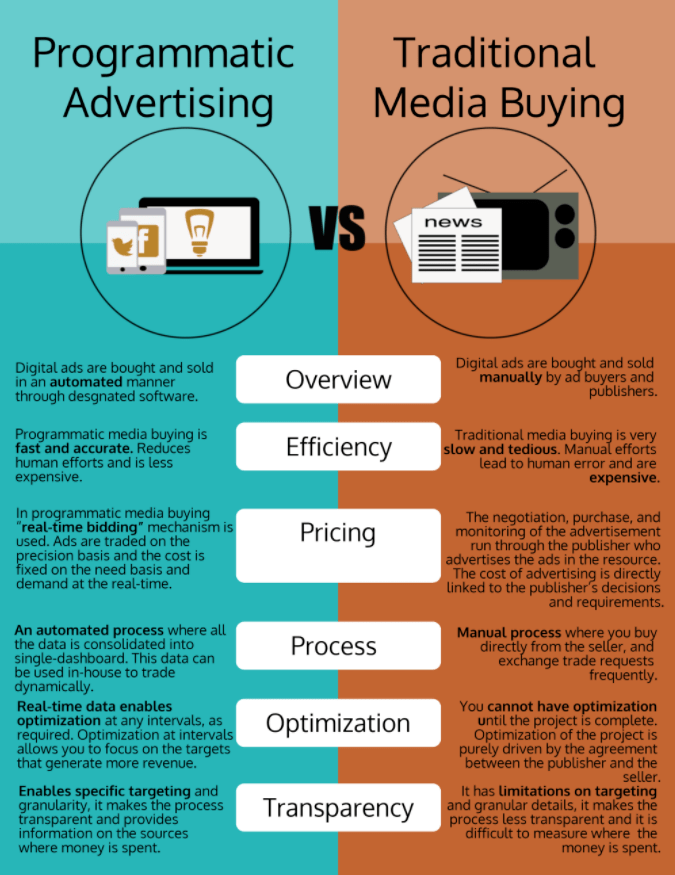
The Programmatic Advertising Process
A set amount of impressions would be promised to the advertiser – and everyone was happy.
It was a time consuming and clunky process. As more and more people joined the online revolution, publishers selling ad space became a dime a dozen and a lot of them got stuck with unsold inventory.
It was inevitable that a better system would be created to solve this issue.
How Programmatic Advertising Works From Start to Finish
When clients are curious about how the process goes, they usually ask
something like –
“How does programmatic advertising work… from the beginning? Let’s say I see an ad online…how did that happen from a programmatic perspective?”
Here’s what typically happens:
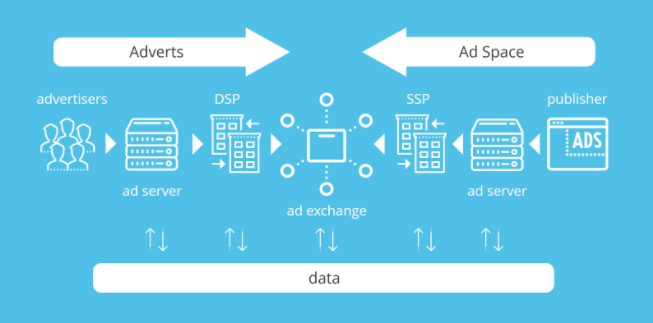
Target User
The programmatic advertising process kicks off the moment a target user, or consumer, lands on a new website. What happens next is an automated process that takes mere milliseconds, in real time.
Supply Side Platform
The website that the target user has landed on is a publisher. Publishers are the sellers and media owners on the internet.
Publishers use supply side platforms (SSPs) to offer their supply of advertising space (or inventory) to advertisers.
These SSPs are automated software systems that use algorithms to communicate data to exchanges and Demand Side Platforms (DSPs).
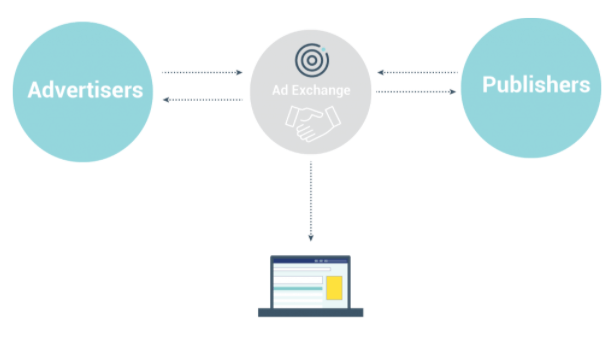
The publisher’s SSP recognizes that a new target user has landed on its website – it pings the ad exchange with a request for an ad to fill their available ad space.
Ad Exchange
An ad exchange is an independent digital marketplace that deals in ad space – and acts as the go-between for SSPs and DSPs. Often, both of these have ad servers they use to distribute their ads.
The exchange receives the prompt from the publisher’s SSP, and sends a request for bids to a huge amount of registered demand side platforms (DSPs).
*Ad exchanges aren’t the same as ad networks, but they do work together sometimes.
Demand Side Platforms
Demand Side Platforms (DSPs) represent the interests of advertisers. It’s their job to find the best possible placement for their client’s adverts.
They do this using unique software that automates the process.
Once the bid request is received by the DSPs, a real-time auction happens.
Real-Time Auction
During the real-time auction – which is also known as real-time bidding – the DSPs process a ton of metadata, which helps them understand the value of the ad placement, in relation to their clients targeted ad campaigns.
Using their own proprietary algorithms, the DSPs will understand what the bid opportunity is worth to their clients. Their interest level is aggregated into a bid amount, which is then communicated to the ad exchange.
Ad Exchange
Target User
That advert is immediately placed in the open ad space on the website. The mission is for this highly targeted ad to achieve its advertising goal – catch the attention of the right user at the right moment.
This entire programmatic advertising process happens in one tenth of a second. Wow!
The programmatic ad process allows advertisers to control who sees their ads, lets publishers and their SSPs sell the exact amount of available inventory – and it puts super-relevant ads in front of the consumer.
The Elements of Programmatic Advertising
Programmatic advertising is one of the most intelligent, evidence-based systems we’ve been able to create in the marketing niche so far. Using data and proprietary algorithms, we can drastically improve the impact of an advert – which increases sales.
With programmatic technology, advertisers are able to show the right advert, at the right moment, to the right target user.
It’s an optimized process that uses several modern elements to produce improved results for the advertiser, the publisher and the consumer involved.
This kind of digital advertising is deliberate and it’s based on big data.
People on both ends of buying and selling in this case use software to crunch enormous amounts of data, make sense of it, and then use it for better decision-making.
Programmatic advertising works across a wide variety of advertising platforms.
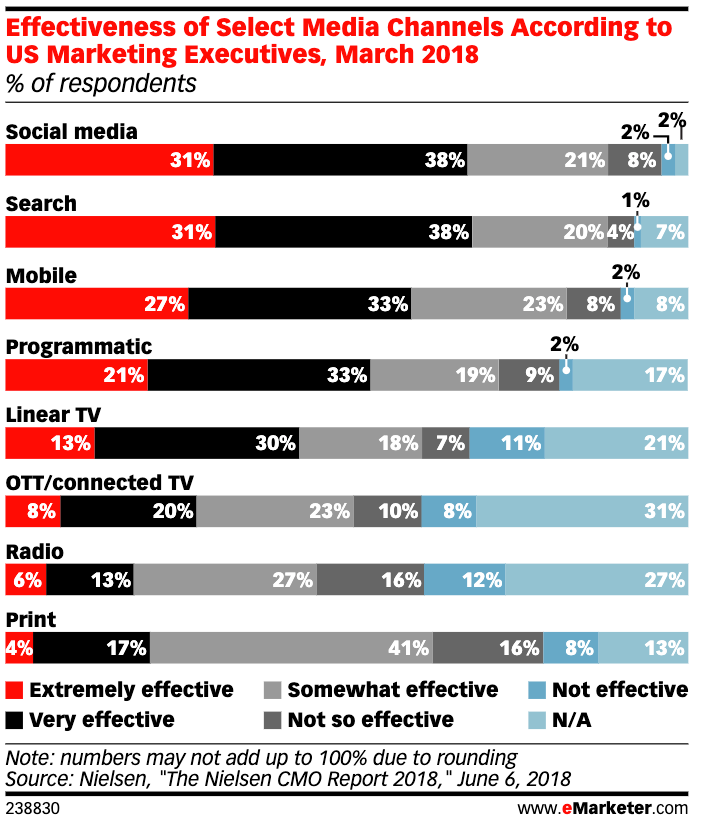
In a recent Nielsen CMO Report, about half of all marketing executives agreed that programmatic advertising was extremely, or very effective.
Now you understand the basic programmatic process.
There are some key elements in this process that will help you understand how it works. Let’s break them down and explain them one by one!
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
The two core technologies impacting programmatic advertising are artificial intelligence and machine learning. If you don’t know what they are, you’re always going to be scratching your head about how programmatic display ads work.
Let’s get some clarity on how these work in advertising.
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
AI is more of a concept than a system.
It’s used to describe software that can perform human-like tasks and make adjustments along the way. These are machines that can learn from experience.
So, AI integrates non-human intelligence into a system that has already been designed for a purpose. AI in its simplest form is just a set of algorithms.
Collected together we call these neural networks – but essentially, they’re just math formulas, calculations and problem solving operations.
Loads of AI algorithms are capable of learning from data, and these are the ones called machine learning algorithms.
Machine learning is a branch of artificial intelligence, and when applied in a system – it allows that system to learn and improve from experience, without human intervention.
So – it’s a type of algorithm that learns things.
How Does Artificial Intelligence Work in Advertising?
Artificial intelligence in digital advertising has shaped the modern programmatic landscape.
AI shows up throughout the programmatic process, but the area you should care about most – is with your DSP or demand side platform.
AI helps your DSP serve highly relevant, targeted messages to your consumers, on the right platforms, at the best times possible. Using the huge amount of data available, the AI has insight into what to do, based on predictive models – that amount to better choices for your ads.
The AI works blindingly fast (it’s a machine after all) – which is how real-time bidding is possible.
So it’s the AI that makes it possible for your ads to be targeted, relevant and automated! It’s software that intelligently buys and sells your ads, better and faster than any human could.
Optimizing Your Campaigns With Real-Time Bidding
The next element of programmatic advertising is the real-time auction.
Advertisers need to buy ad space from publishers. In programmatic advertising, real-time bidding is what happens once the demand side platforms have received the request for bids.
Bids are made for impressions, which are bought and sold at these auctions. One impression (CPI) means that the ad has been displayed once on the website.
Editor’s Note: Fun fact: CPM stands for cost per mille – or cost per thousand impressions.
Mille is Latin for a thousand. To learn more about advertising lingo, check out our Advertising Dictionary.
The publishers set a floor price (or lowest possible bid amount) and then prices fluctuate, according to the rate of demand. So, if lots of advertisers want a particular ad space – the cost per impression will be quite high.
What makes this process programmatic is the software involved. At no point are people setting bids or negotiating prices like the old days of display advertising. It’s 100% automated.
The fact that software automatically bids based on its AI and machine learning capabilities, is what makes RTB innately programmatic.
This is a highly optimized process that streamlines results for both advertisers and publishers.
Using Data in Programmatic Advertising
How does programmatic advertising work with data?
This is another significant element of programmatic media buying and selling. Data is the thing that intelligent software collects and analyzes – so that it can make good decisions.
It drives the entire process!
But where does this data come from and how is it used?
Data Management Platforms
There are some great DSPs like War Room’s Kedet, which helps advertisers use important data along with their advertising strategies and technology, to strengthen ad campaigns.
DSPs and SSPs tap into data management platforms (DMPs) that collect big data from a vast array of sources, then store and organize it so that insights are at the ready for advertisers.
In a recent report from Salesforce where 900 advertisers were surveyed, there is an average of 5.4-6.2 data sources being used by digital advertisers to inform their software and various strategies.
Data comes from a range of sources:
- Digital and Search Data
- Ad Serving Data
- CRM Data
- Social Media Monitoring Data
- Mobile / Geolocation Data
- Syndicated Media Measurement Data
First Party Data
First-party data is widely accepted as the highest value form of data. It includes information from advertiser analytics, search, display and email campaign data, transaction data, CRM data and of course – cookie-based data.
When your consumer accepts cookies from a website for example, they’re giving that website permission to track, record and analyze everything they do on the site.
This gives advertisers a better idea what the consumer is searching for, so that ads can be tailored to their unique behavioral preferences.
- Cookies help with retargeting
- Storing user preferences
- Record user activity
- Store stateful data (like what you’ve added to a wishlist or cart)
A lot of first party data is used to figure out demographic details like age, gender, location, interests and general behavior.
The accuracy of this data is hands-down the most important thing to advertisers. A recent survey had 84% of respondents say that accuracy was critical to purchasing decisions.
Second Party Data
Second party data still has value in advertising, and is usually made up of data from other advertisers that can be purchased from the DMP.
A good example is a company that sells cars, buying profile data from a company that sells car accessories. The two have similar customers, and insights can be gained through these sorts of cross-market investigations.
Third Party Data
Data management platforms and other data collection agencies collect third party data to sell to advertisers. A lot of cookie-based data for example, is anonymous – but has value in volume.
Targeting and Relevance in Your Ad Campaigns
Programmatic targeting refers to the automated data-informed ad strategy that targets your consumers.
Once advertisers (or publishers) have data, and data insights – ads can be targeted for better performance. This means ads that have a higher return on investment for advertisers.
There are several targeting strategies that are used to get advertisers results online.
Let’s briefly explore a few, to give you context.
Contextual Targeting
Contextual targeting focuses on the type of content users are browsing on the internet.
Programmatic contextual targeting lets the advertiser better understand which types of content, on which pages consumers are using or looking at.
Retargeting
Retargeting focuses on re-engaging the consumer who has already visited a specific website – and left. Their actions and history are captured on the advertiser’s website, then – ads are shown to them based on their preferences – even as they look at other sites online.
That’s why you’ll notice products you’ve clicked on, looked at, or put in your shopping cart following you around the internet.
Audience Targeting
Audience targeting focuses on specific sets of demographic data, interests and behaviors. It’s usually extremely customized to an individual group’s needs.
If you’re a fashion advertiser, and your main demographic is unmarried, 25 year old, cat enthusiasts who love shoes – this kind of targeting is highly effective for your cat-styled shoe advert.
Geotargeting
Also called geofencing, geotargeting focuses on people in a specific location. Mobile campaigns work well with these perimeter-orientated ads, and with local marketing.
Website / App Targeting
Website and app targeting focuses on platform-specific advertising. If you know you’re reaching out to consumers on Facebook Mobile or on an app for example, then you can tailor your creative campaigns for these platforms.
The Creative Side of Programmatic Campaigns
Programmatic creative refers to data-informed, software-assisted adverts that are made to be extremely relevant for consumers.
It makes sense that in order to really reach and convert consumers, the ads themselves have to be as optimized as the targeted delivery process. After all, it’s the message that converts people.
Intelligent creative adapts and becomes personalized to the individual who is viewing it – taking advantage of those machine learning algorithms we learned about earlier.
The insights gleaned from the customer, become part of the creative brand message.
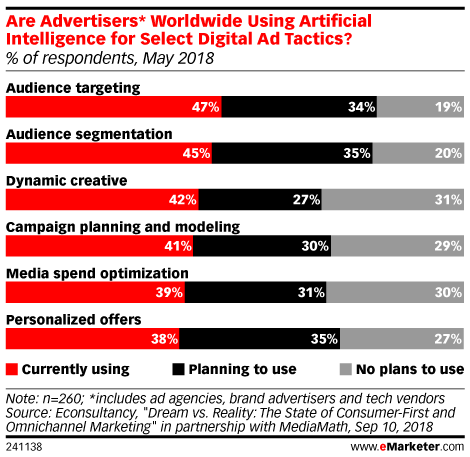
In one study from , 42% of advertisers said they were currently using AI-driven dynamic creative (a type of programmatic creative) in their marketing campaigns.
Ad campaigns that use programmatic creative create a valuable feedback loop for optimizing future campaigns. Advertisers will learn which ads work best, faster using these evidence-based methods.
Achieving Campaign Goals With Programmatic
So, how does programmatic advertising work to improve campaign goals?
Every advertiser that approaches programmatic, does it with a desire to optimize their ad spend, and get more impressions, for less. This means setting the right goals and key performance indicators.
Partnering with the right DSP is why this is so important. Your agency will help you understand what your goals are, and how to achieve them using programmatic means.
Different goals will result in your agency creating different programmatic creative, and picking the right strategies to target your relevant audiences.
Key performance indicators can then be assigned to your goal, to measure outcomes.
Using set inputs, your programmatic advertising team will then automate the process of placing your ads, in real time. The longer you run ads, the more you will learn – and sell.
Sharing How Programmatic Advertising Works
Programmatic advertising works to streamline your advertising campaigns from day 1. Using AI, big data and real-time bidding, your ads will outperform anything that could be achieved manually.
Programmatic isn’t some far off future concept, it’s happening now. The sooner your company jumps on board and partners with the right agency, the better.
Your ad results will improve over time, due to machine learning and AI technology. That’s how programmatic advertising works.
When first learning about automation, you may have a lot of questions about the technology. Hope this guide gave you some insight on how the system works!
Are you looking for a programmatic advertising partner?
What Have We Learned?
- Digital ads are everywhere. An average American sees an ad every 15 seconds but ¼ of all advertising budget is wasted. Marketers have began utilizing programmatic advertising, which is automated buying and selling of digital ad space online via artificial intelligence.
- From targeting users, both Supply Side Platforms and Display Side Platforms conduct ad exchange through real-time bidding. This allows advertisers to have transparency and control over the audience of their ads. Thus hyper-targeted and relevant ads are seen by the public.
- Marketers find programmatic advertising to be extremely effective.
Artificial Intelligence conducts real-time bidding and is how relevant ads are served to consumers at the appropriate and effective time and place. - Data comes from first, second and third-party cookies. First party cookies help with retargeting and useful data like demographics and user preferences. Second-party cookies are made up of data from advertisers that can be bought from a Demand Side Platform. Third-party cookies are often anonymous data that data collection agencies collect to sell to advertisers.
- Advertisers use a variety of strategies to get results online. Such as: contextual targeting, retargeting, audience targeting, geotargeting, website/app targeting etc.
- Advertisers leverage data to create highly relevant ads to consumers. Most of the data insights come from AI-driven, machine-learning algorithms.
- Partnering with an advertising agency means they will assist you with setting up appropriate KPIs for your business goals. This means creatives will vary. Then, your ads will be plugged in and ran, all automated. Note that the longer your ads are run, the more the machine learns and data collected, and the longer you sell!
- Programmatic advertising streamlines the entire process of your campaigns from Day 1. It’s a technology-driven trend in the marketing industry only to continue to boom!